Voyager 1 detects persistent hum
The Voyager 1 probe recently picked up humming sound. The scientists have named this as “Plasma Wave Emission”. This humming sound has been interpreted as interstellar gas activity. Moving forward, the Voyager 1 will help scientists to understand the interactions between solar winds and the interstellar medium. The hum was of narrow frequency bandwidth.
About the discovery
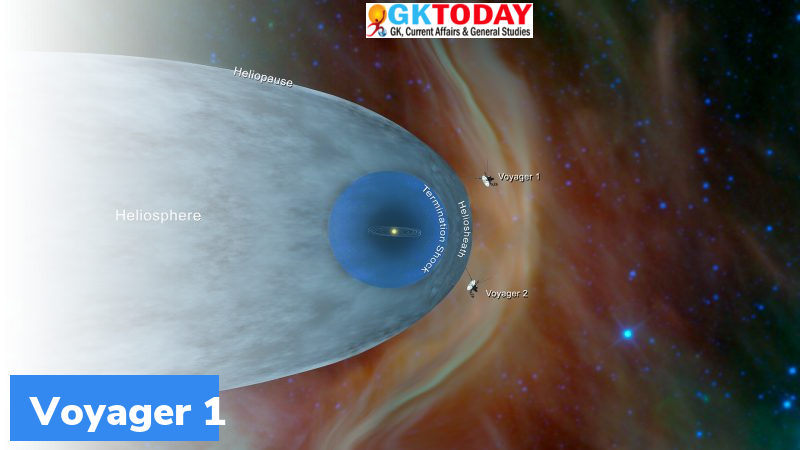
The discovery of humming sound was made by the Plasma Wave System Instrument of Voyager 1. This sound was heard after Voyager 1 exited the heliosphere and entered the interstellar space.
The first humming sound was heard after three months the Voyager 1 exited heliosphere. The second sound was heard after six months the Voyager 1 exited the heliosphere. However, the second sound was louder. With this, the scientists conclude that the interstellar medium is getting thicker at faster rate.
What is interstellar medium?
Interstellar medium is the radiation and matter that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This medium consists of gas in molecular, atomic or ionic form.
Voyager 1
- The Voyager 1 was the first spacecraft to enter the heliosphere of the sun in 2012.
- The Voyager 1 was launched in 1977.
- It was launched to study the outer solar system and planets such as Saturn and Jupiter on its way.
- Voyager 2 is called the twin of Voyager 1.
- After operating for 44 years, it is still communicating with the Deep Space Network of NASA. The Deep Space Network of NASA is a worldwide space communication network located in the US, Spain and Australia.
Month: Current Affairs - May, 2021