Types of Pollination
In flowering plants, pollination refers to transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma.
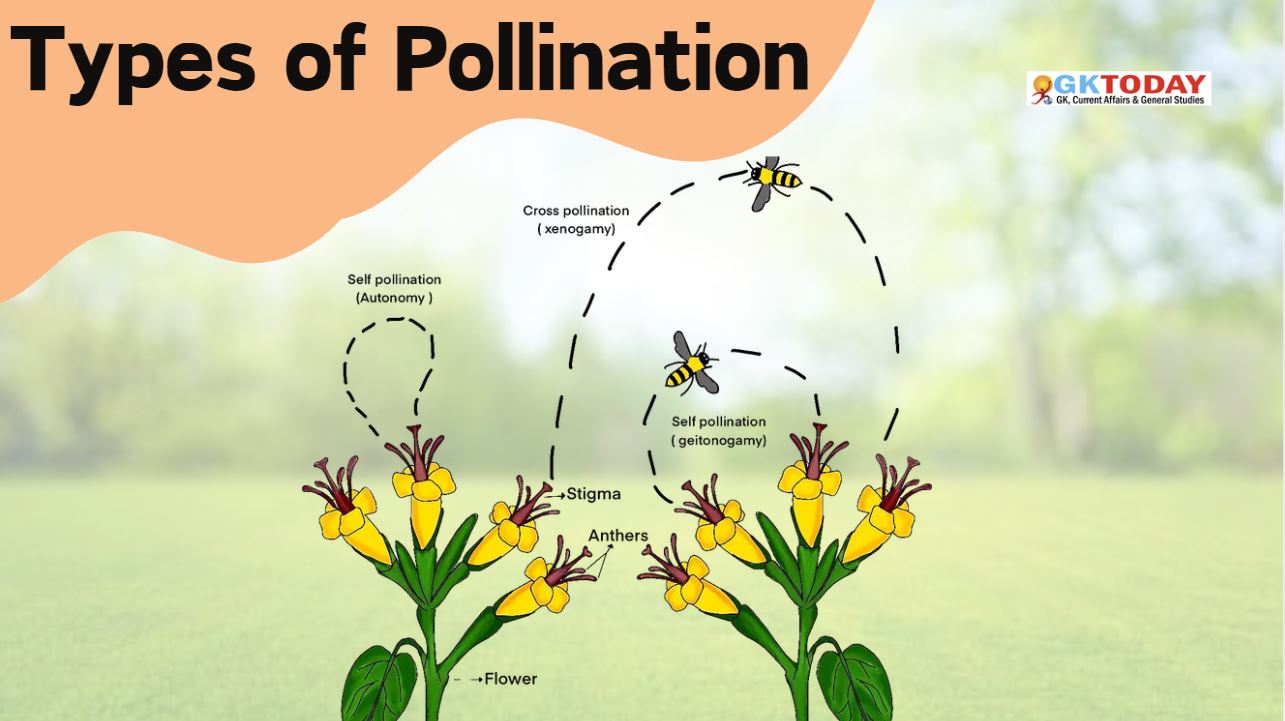
Pollination taking place in a single flower is called self pollination, while pollination taking place between two flowers is called cross pollination. If the cross pollination is between flowers of a same plant, it will be called Geitonogamy, while if it takes place between two separate plants, it will be called as Xenogamy. In some plants, the flowers are bisexual and closed called Cleistogamous. Here only self pollination takes place.
Insects (Entomophily) can facilitate the pollination, similarly can Wind (anemophily), Water (Hydrophily), Animals (Zoophily). Further, Hummingbirds, bats, monkeys, marsupials, lemurs, bears, rabbits, deer, rodents, lizards and other animals are common animals that carry pollens and help in pollination.
Pollination by Bats
Pollination done by Bats is called chiropterophily. Many fruits are dependent on bats for pollination, such as mangoes, bananas, and guavas. Bat pollination is an integral process in tropical communities with 500 tropical plant species completely, or partially, dependent on bats for pollination.
Pollination by Birds
The term ornithophily is used to describe pollination specifically by birds. Hummingbirds, sunbirds, honeyeaters, flowerpeckers, honeycreepers, and bananaquits are examples. Plants pollinated by birds often have brightly colored diurnal flowers that are red, yellow, or orange, but no odor because birds have a poor sense of smell. Other characteristics of these plants are that they have suitable, sturdy places for perching, abundant nectar that is deeply nested within the flower. Often flowers are elongated or tube shaped. Also, many plants have anthers placed in the flower so that pollen rubs against the birds head/back as the bird reaches in for nectar.
Pollination by Lizards
Although lizard pollination has historically been underestimated, recent studies have shown lizard pollination to be an important part of many plant species’ survival. Not only do lizards show mutualistic relationships, but these are found to occur most often on islands. The lizard Hoplodactylus is only attracted by nectar on flowers, not pollen.