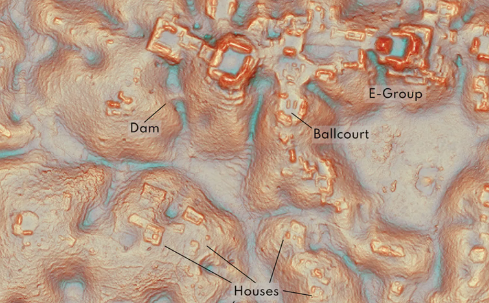
Scientists Discover Lost Mayan City Using LiDAR
Scientists announced the discovery of a lost Mayan city in the Mexican jungle. This finding was made possible through the use of LiDAR technology. The dense vegetation that typically obscures archaeological sites was penetrated, revealing ancient structures below.
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It is a remote sensing method. LiDAR uses light pulses to measure distances. Typically, a sensor is mounted on an aircraft. This technology can create detailed 3-D models of the Earth’s surface. The US Geological Survey states that LiDAR can achieve vertical accuracy of up to 10 cm.
Components of LiDAR
LiDAR systems consist of three main components: a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. Each part plays a crucial role in capturing data from the environment.
How Does LiDAR Work?
The process begins with the laser. It emits rapid pulses of light towards the ground. These pulses travel down and hit various surfaces, such as trees, buildings, and the ground itself. When the light hits an object, it reflects to the sensor. The scanner collects this reflected light. The time it takes for the light to return is measured. This time measurement helps calculate the distance to the object. The GPS receiver adds location data to the measurements. It ensures that each point collected by the LiDAR system corresponds to a specific geographic location.
Applications of LiDAR
LiDAR has many uses. It is commonly employed in forestry to assess tree heights and density. It is also used in urban planning to map infrastructure. Archaeologists use LiDAR to discover and map ancient sites, like the recently found Mayan city. In addition, LiDAR aids in flood modeling and assessing changes in landscapes. Its high-resolution data helps in understanding environmental changes over time.
Advantages of LiDAR
LiDAR offers several advantages over traditional surveying methods. It can cover large areas quickly. It does not require physical access to the ground, making it ideal for dense forests or inaccessible regions. The accuracy of LiDAR data is also an important benefit. It provides detailed information about the terrain, which is invaluable for various scientific and engineering applications.
Limitations of LiDAR
Despite its advantages, LiDAR has limitations. It can be expensive to deploy. The technology requires skilled operators and sophisticated equipment. Additionally, LiDAR may struggle in certain weather conditions. Heavy rain or fog can obstruct the laser pulses, reducing data quality.
Future of LiDAR Technology
The future of LiDAR looks promising. Advances in technology are making it more accessible and cost-effective. Researchers are continually improving data processing methods. As LiDAR becomes more widespread, its applications will expand. It will likely play a vital role in environmental monitoring and archaeological discoveries. LiDAR is a powerful tool for mapping and analyzing the Earth’s surface. Its recent application in uncovering a lost Mayan city marks its potential in archaeology and beyond.
Month: Current Affairs - November, 2024
Category: Science & Technology Current Affairs