Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project
The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP) is initiative aimed at enhancing irrigation in Rajasthan. This project will impact 23 districts and is crucial for providing water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use. However, it poses environmental challenges, particularly regarding the Ranthambhore tiger reserve.
Project Context
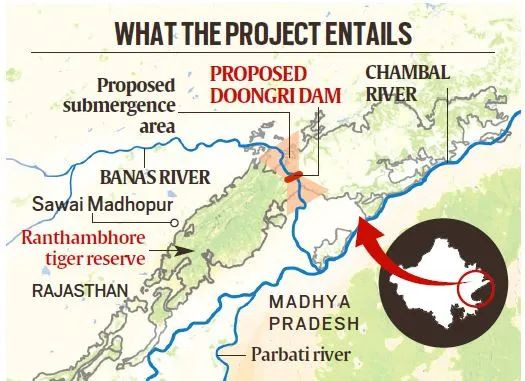
The PKC-ERCP will submerge 408.86 sq km of land, including 37 sq km of the Ranthambhore tiger reserve. This reserve is home to 57 tigers and is vital for wildlife conservation. The project aims to channel surplus water from the Chambal river basin, benefiting approximately 3.45 crore people in Rajasthan.
Dam Specifications
The project includes a 39-metre-high dam across the Banas river, located near Doongri, about 30 km from Sawai Madhopur. The dam will be 1.6 km long and is designed to support the irrigation needs of the region. However, its construction will disrupt the north-south animal dispersal route within the tiger reserve.
Environmental Concerns
Conservationists have raised alarms about the project’s impact on habitat connectivity and the carrying capacity of the tiger reserve. The submergence of land is expected to adversely affect the ecosystem. Experts suggest that high-value forests should be avoided in dam designs to mitigate these impacts.
Government Response
Baleshwar Thakur, director general of the National Water Development Agency, stated that multiple agencies will evaluate the Detailed Project Report (DPR) before approval. He assured that measures would be taken to minimise the impact on the tiger reserve. If unavoidable, compensatory measures will be implemented, similar to those in previous projects.
Project History
The Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project was initially conceived in 2017. After political changes, the project was expanded to include the PKC initiative. An MoU was signed by Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh with the Centre for the revised project. The DPR for the Rajasthan segment is set to be submitted to the Central Water Commission soon.
Future Developments
Phase One of the PKC-ERCP includes constructing the Doongri dam and five barrages. These structures aim to enhance the water supply for irrigation purposes. The deadline for completing this phase is set for 2028, with ongoing assessments to ensure minimal environmental disruption.
- Ranthambhore was declared a tiger reserve in 1974.
- The PKC-ERCP will affect 23 districts in Rajasthan.
- 57 tigers currently inhabit the Ranthambhore tiger reserve.
- The Doongri dam is 39 metres high and 1.6 km long.
- Phase One of the project includes five barrages in Rajasthan.
Conservation Strategies
Environmental experts recommend that if submergence occurs, compensatory land should be designated to offset the losses. The focus should be on preserving the core areas of wildlife sanctuaries to maintain biodiversity. Future project designs must consider the ecological significance of high-value forests to prevent irreversible damage to natural habitats.
Month: Current Affairs - January, 2025
Category: Environment Current Affairs