Rainfall Trends and Vegetation Changes in India
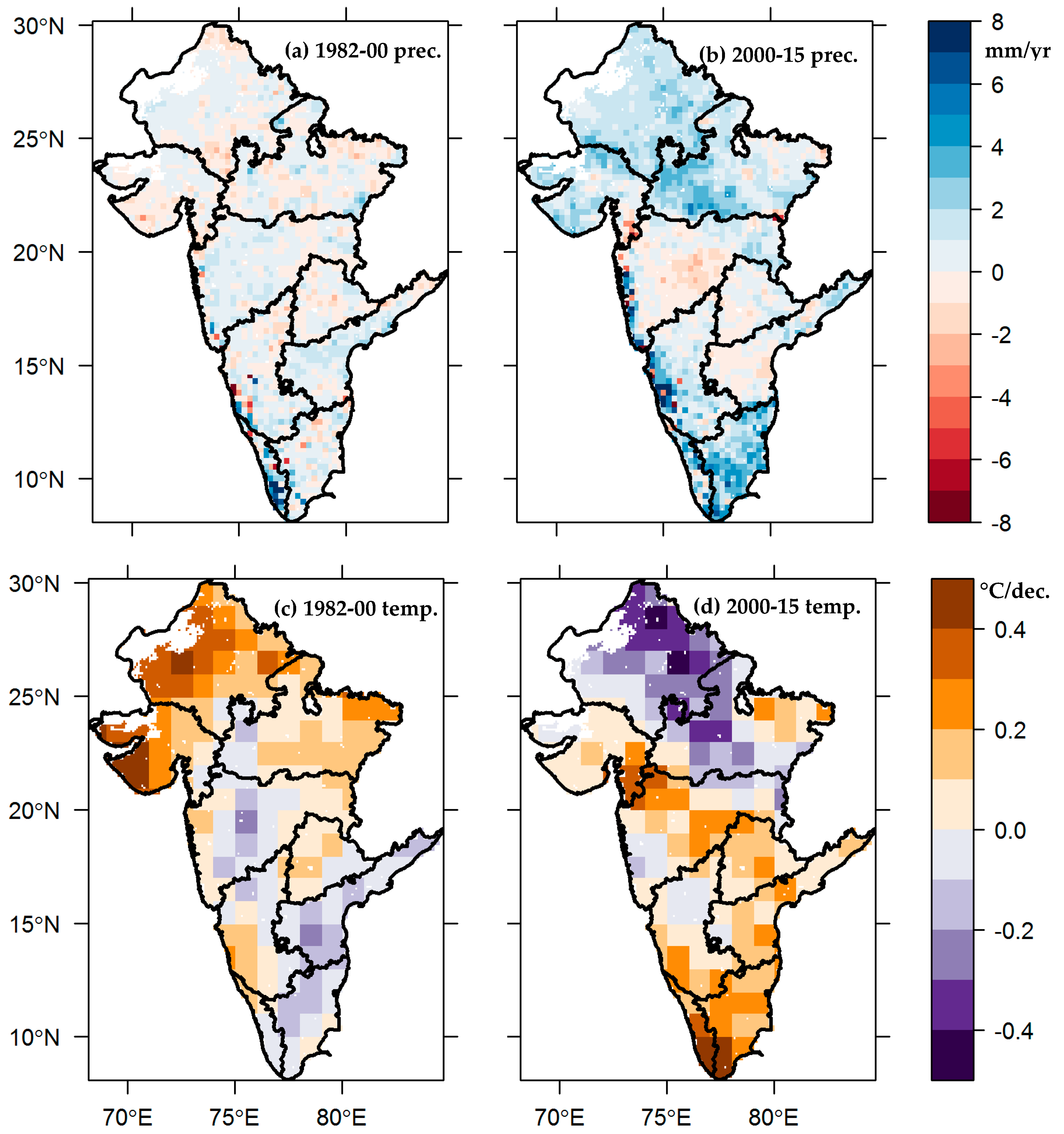
Recent studies have revealed shifts in rainfall patterns across India between 2011 and 2020. The findings indicate that while some regions have experienced increased rainfall, others have seen a decline. This analysis is based on data from the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP-ISRO), a collaboration between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
Rainfall Variations Across Regions
The study marks that west-central India saw an increase of approximately 2 mm of rainfall per day during the last decade. Conversely, eastern parts of India experienced a decrease of about 1 mm per day. The Indo-Gangetic Plain and southern regions also saw slight increases but not as pronounced as those in the west-central area.
Vegetation and Soil Moisture Correlation
The increase in rainfall in west-central India correlates with a rise in vegetation cover. The Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) values increased from around 0.2 to 0.4, indicating greater vegetation density. This increase in vegetation leads to higher transpiration rates, contributing to atmospheric moisture during the summer monsoon. Additionally, soil moisture content in this region has risen, further supporting the observed rainfall trends.
Shifts in Rainfall Timing
The timing of peak rainfall has also shifted. In the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the peak rainfall now occurs 2-4 hours earlier than in the previous decade. In contrast, west-central India has seen a delay of 1-2 hours in peak rainfall. This variation is influenced by aerosol levels, which affect atmospheric conditions and rainfall patterns.
Impact of Aerosols on Rainfall
Higher aerosol concentrations in the Indo-Gangetic Plain are linked to earlier peak rainfall. Aerosols absorb and scatter solar radiation, altering atmospheric stability and influencing rainfall timing. The study suggests that similar mechanisms may apply in other polluted regions, where aerosols can modulate rainfall behaviour.
Implications for Climate Studies
These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of climate dynamics in India. They highlight the importance of monitoring vegetation cover and soil moisture as indicators of changing rainfall patterns. This research also puts stress on the need for continued studies on the impact of aerosols on weather phenomena.
Month: Current Affairs - April, 2025
Category: Environment Current Affairs