Over, Under, and Optimum Population
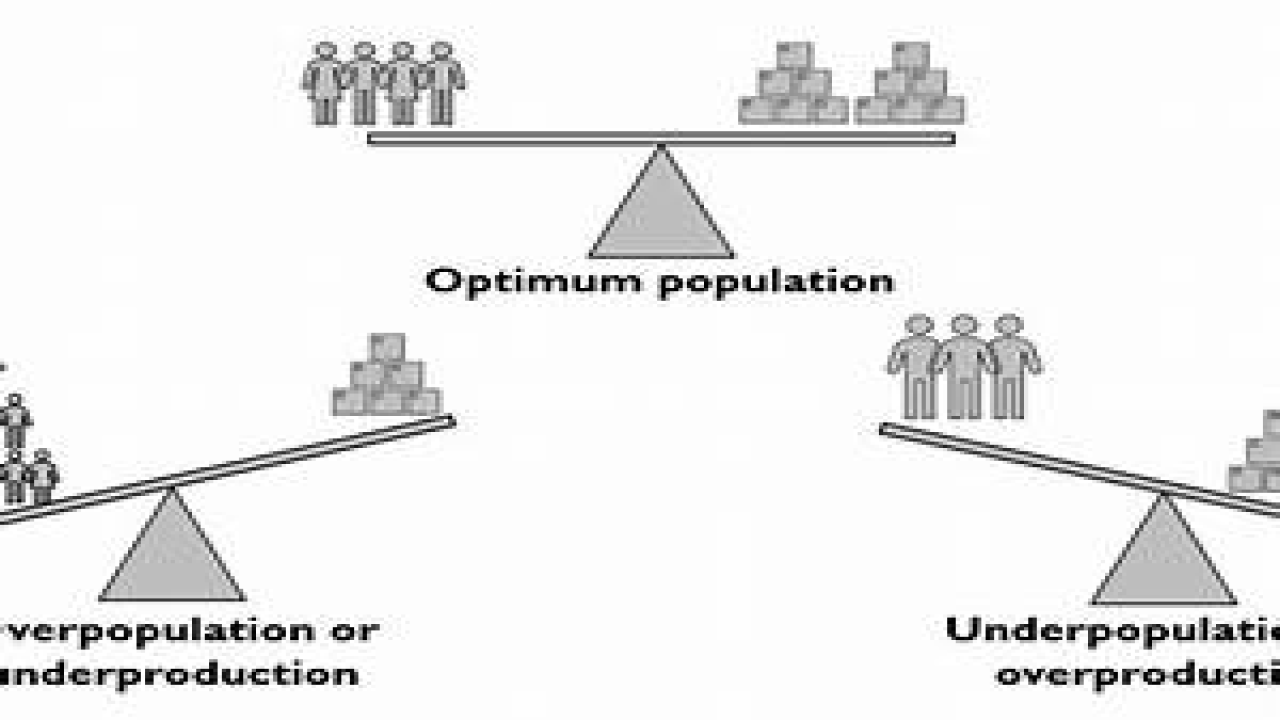
The concepts of over, under, and optimum population are important in understanding the relationship between population and resources. Overpopulation occurs when the number of people in a given area exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment, while underpopulation occurs when there are not enough people to fully utilize the available resources. Optimum population is the ideal number of people that can live in an area without causing environmental or social problems.
Meaning of Over, Under, and Optimum Population
Overpopulation refers to a situation in which the number of people in a given area exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment. This can lead to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and social and economic problems. Underpopulation refers to a situation in which there are not enough people to fully utilize the available resources. This can lead to economic stagnation, social isolation, and cultural decline. Optimum population refers to the ideal number of people that can live in an area without causing environmental or social problems.
History of Over, Under, and Optimum Population
The concept of overpopulation can be traced back to the writings of Thomas Malthus, who argued that population growth would eventually outstrip the availability of food and resources. The concept of underpopulation is relatively new, as historically, populations have tended to grow rather than decline. The concept of optimum population emerged in the mid-20th century, as scholars and policymakers began to explore the relationship between population and resources.
Types of Over, Under, and Optimum Population
Over, under, and optimum population can be classified into several types, including:
- Regional: Over, under, and optimum population can vary by region, with some areas experiencing high levels of population growth and others experiencing population decline.
- National: Over, under, and optimum population can vary by country, with some countries experiencing rapid population growth and others experiencing population decline.
- Global: Over, under, and optimum population can also be viewed at the global level, with some regions experiencing rapid population growth and others experiencing population decline.
Examples of Over, Under, and Optimum Population
Here are some examples of over, under, and optimum population:
- Overpopulation: The population of India is expected to surpass that of China by 2027, leading to concerns about the impact of rapid population growth on the environment and resources.
- Underpopulation: The population of Japan is declining, leading to concerns about the impact of an aging population on the economy and social structure.
- Optimum Population: The population of Denmark is considered to be at an optimum level, as it is able to sustainably utilize its resources without causing significant environmental or social problems.
Issues with Over, Under, and Optimum Population
Despite the importance of the concepts of over, under, and optimum population, there are several issues associated with the topic, including:
- Definition: The definition of over, under, and optimum population can vary depending on the context and the criteria used to measure population and resources.
- Data Availability: The availability of reliable and accurate data on population and resources is a challenge for policymakers and researchers.
- Political Implications: The concepts of over, under, and optimum population have political implications, as they can be used to support or challenge policies related to population growth, immigration, and resource management.
- Environmental Concerns: Overpopulation can lead to environmental degradation and resource depletion, while underpopulation can lead to the abandonment of land and the loss of biodiversity.
- Economic Issues: Overpopulation can lead to economic challenges, such as unemployment, poverty, and social inequality, while underpopulation can lead to economic stagnation and a decline in economic growth.Social Implications: Overpopulation can lead to social issues such as overcrowding, lack of access to healthcare and education, and social unrest. Underpopulation can lead to social isolation, declining communities, and cultural decline.
- Resource Management: Overpopulation can lead to the depletion of resources such as water, food, and energy, while underpopulation can lead to the underutilization of resources and a lack of investment in infrastructure and development.