Heat budget of the earth
The heat budget of the Earth refers to the balance of energy that enters and leaves the planet’s atmosphere. This balance is critical for maintaining stable climate conditions and sustaining life on Earth.
What is the Heat Budget of the Earth?
The heat budget of the Earth refers to the balance of energy that enters and leaves the planet’s atmosphere. This energy is derived from the sun, which radiates heat and light energy towards the Earth. Some of this energy is absorbed by the atmosphere and the Earth’s surface, while the remainder is reflected back into space. The heat budget of the Earth is a complex system that is influenced by a range of factors, including atmospheric gases, clouds, and the Earth’s rotation.
Components of the Heat Budget of the Earth
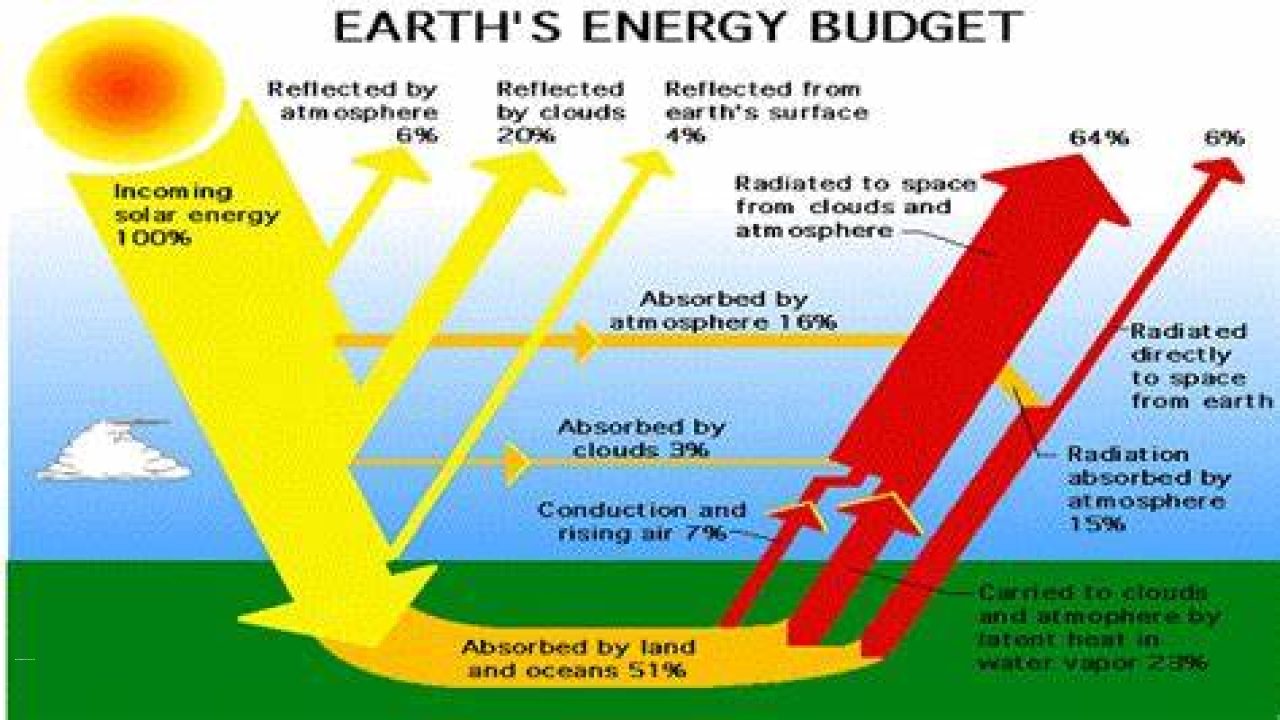
The heat budget of the Earth is made up of several components, including:
- Incoming Solar Radiation: This is the amount of energy that the Earth receives from the sun. It is also known as solar insolation and varies with latitude and time of day.
- Reflected Solar Radiation: This is the amount of solar radiation that is reflected back into space by the Earth’s atmosphere and surface. The amount of reflected solar radiation depends on the albedo, or reflectivity, of the Earth’s surface.
- Absorbed Solar Radiation: This is the amount of solar radiation that is absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and surface. This absorbed energy is responsible for warming the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
- Outgoing Thermal Radiation: This is the amount of energy that is emitted by the Earth’s surface and atmosphere as heat. This heat is radiated outwards into space, balancing the incoming solar radiation and maintaining a stable climate.
Factors that Influence the Heat Budget of the Earth
The heat budget of the Earth is influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Greenhouse Gases: Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, absorb and re-radiate heat energy in the atmosphere. This can lead to an increase in the Earth’s temperature, known as the greenhouse effect.
- Cloud Cover: Clouds reflect solar radiation back into space, reducing the amount of energy that is absorbed by the Earth’s surface.
- Land and Ocean Surfaces: Land and ocean surfaces have different albedos, which affects the amount of solar radiation that is absorbed and reflected.
- Atmospheric Circulation: The movement of air masses in the atmosphere can affect the distribution of heat energy across the planet.
The Importance of the Heat Budget of the Earth
The heat budget of the Earth is a critical component of the planet’s climate system, influencing weather patterns and climate conditions across the globe. Understanding the heat budget of the Earth is essential for predicting changes in global climate patterns, including the effects of climate change. By understanding the factors that influence the heat budget of the Earth, scientists can develop strategies for mitigating the effects of climate change and promoting sustainable development.