Deep Brain Stimulation
Doctors at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) successfully treated a severely depressed patient by identifying and harnessing brain circuits associated with depressed brain patterns. Doctors have tried to re-establish these patterns, which they believe is equivalent to wearing a pacemaker. This work, which marks a milestone in the use of neuroscience to treat psychiatric disorders, was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
About Deep Brain Stimulation
Doctors used an existing technique called deep brain stimulation (DBS) and adapted it to this depressed patient’s case. DBS is a surgical procedure in which electrodes are implanted in specific areas of the brain. These wires or electrodes generate electrical impulses through which abnormal brain activities can be controlled. According to the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS), electrical impulses can also correct chemical imbalances in the brain that cause various conditions.
Components of Deep Brain Stimulation
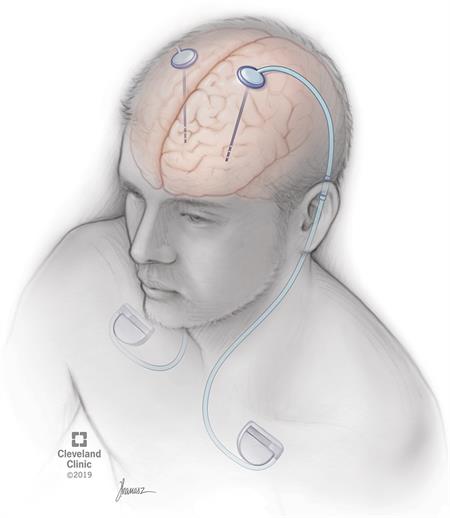
DBS has three components. They are
- The lead or electrode. This is a thin, insulated wire that is inserted through a small opening in the skull and implanted in a specific area of the brain.
- The extension wire which is also insulated and passed under the skin of the head, neck and shoulder and connects the electrode to the third component of the system.
- The internal pulse generator (IPG) is the third component. It is typically implanted under the skin on the upper chest.
Treatments using Deep Brain Stimulation
Conditions traditionally treated with DBS include epilepsy, dystonia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, essential tumorand Parkinson’s disease. However, previous clinical studies of DBS have shown limited success in treating depression, as most devices can only provide constant electrical stimulation to one area of the brain.
During this treatment, UCSF doctors fitted a new DBS device that stimulated the brain when it recognized the depressive pattern. In addition, the medical team had found a neuronal biomarker that indicated the appearance of symptoms. With the custom-made DBS device, they were able to stimulate another area of the brain, which in turn created instant therapy for the brain.
Conclusion
In the year 1991, the modern DBS was developed in France by professor of neurosurgery Dr. Alim Louis Benabid. With advances in surgical practice and technology, this therapy has continued to improve and it is now a standardized procedure in more than 1,200 hospitals around the world in more than 70 countries.