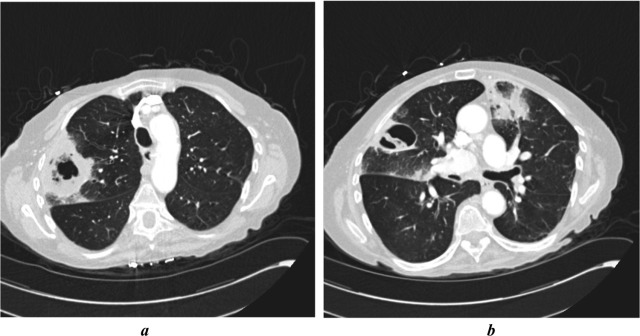
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
The health of tea plantation workers in Assam has come under scrutiny due to a recent study denoting risk of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA). This life-threatening fungal infection primarily affects tuberculosis (TB) survivors. The research was conducted by a team from Assam Medical College and Hospital, revealing alarming prevalence rates among tea workers.
Context of Tuberculosis in Assam
Tuberculosis remains a critical public health concern in Assam. The National Tuberculosis Prevalence Survey (2019-2021) reported a TB incidence of 217 cases per 100,000 population. Contributing factors include poverty, malnutrition, and poor living conditions. These factors create an environment conducive to the spread of TB and its complications.
About Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis is a lung disease caused by the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus.
- It typically affects individuals with pre-existing lung conditions, especially those who have had TB.
- Symptoms include chronic cough, blood in sputum, and fatigue.
- The disease can impair lung function.
Study Findings and Prevalence Rates
- The study examined 128 patients from tea estates in the Dibrugarh district. Researchers found a CPA prevalence of 17.18%.
- Among active TB patients, the prevalence was 18.5%, while it surged to 48.9% in those who had completed TB treatment.
- This indicates a strong link between previous TB infections and the development of CPA.
Demographics and Risk Factors
The mean age of patients was 41.9 years, with a higher incidence in middle-aged males. Smoking was identified as a potential risk factor. Interestingly, a study in Kenya showed a higher prevalence of CPA in non-smokers, indicating that more research is needed to understand the disease’s risk factors.
Global Comparisons and Health Implications
Assam’s CPA prevalence of 60 cases per 100,000 people exceeds the global average of 42. This situation is worse than in several African countries. The high rates of respiratory illnesses among tea workers contribute to lower productivity and increased medical expenses, leading to economic strain on families.
Recommendations
- Researchers recommend routine testing for Aspergillus antibodies in patients showing respiratory symptoms post-TB treatment.
- Early diagnosis can reduce morbidity and mortality associated with CPA.
- Training healthcare providers to recognise CPA symptoms is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Month: Current Affairs - January, 2025
Category: Science & Technology Current Affairs