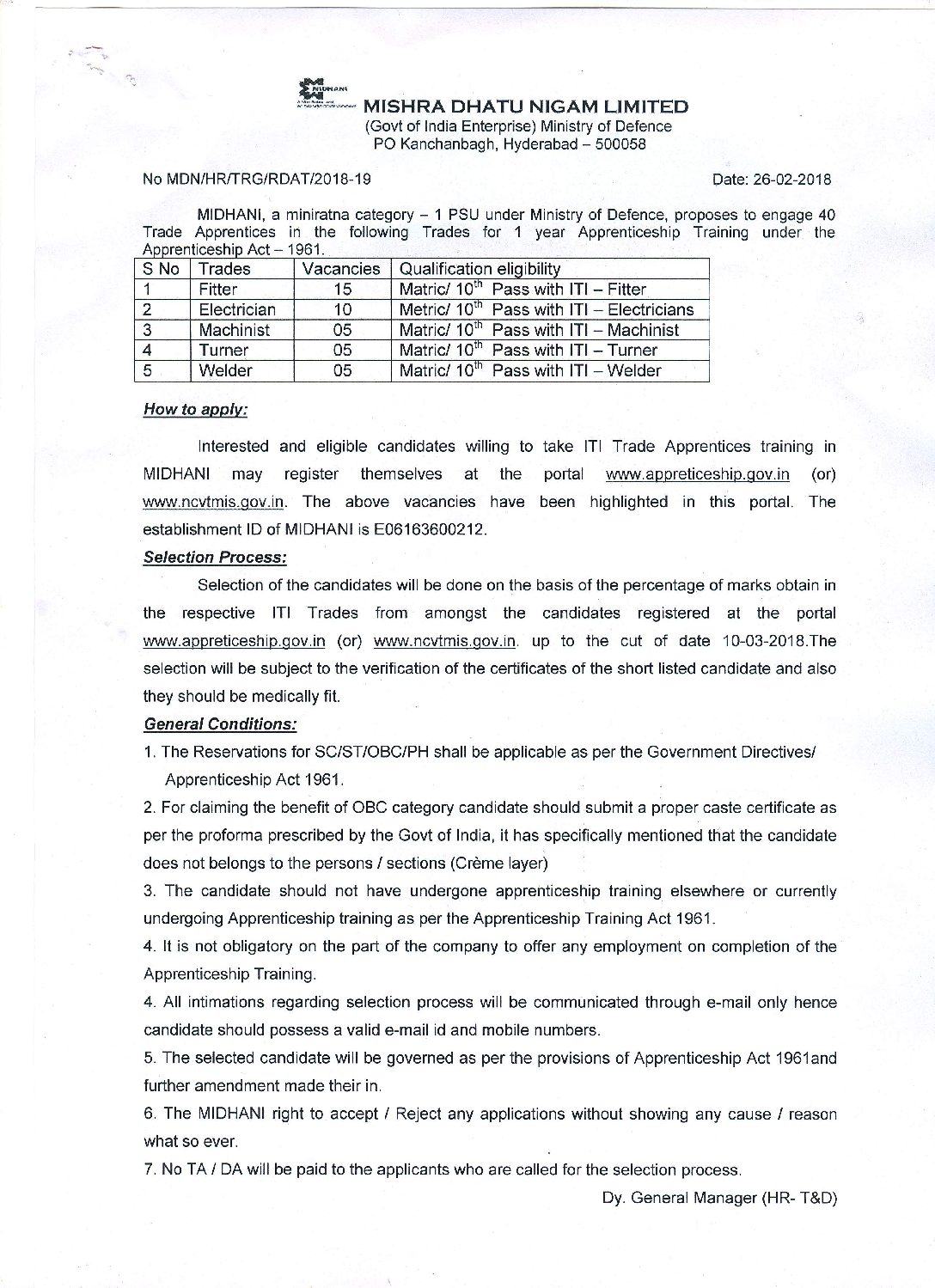
AWaRe to Guide Antibiotic Use
The World Health Organization (WHO) has created a new tool AWaRe (for Access, Watch, and Reserve) to limit the use of drugs associated with the highest risk of resistance and to increase the use of antibiotics in countries where supply and availability are low.
AWaRe Tool
Developed by the WHO Essential Medicines List, AWaRe aims to reduce the spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), antibiotic-related adverse events, and drug costs.
The tool classifies antibiotics into three groups
- Access: Antibiotics to use for the most common and serious infections.
- Watch: ones should be available at all times in the healthcare system.
- Reserve: To be used sparingly or preserved and used only as a last resort.
The AWaRe campaign aims to increase the proportion of global consumption of antibiotics in the Access group to at least 60% and to reduce the use of the antibiotics most at risk of resistance from the Watch and Reserve groups.
The Access antibiotics are at lower risk of resistance as they are narrow-spectrum antibiotics which target a specific microorganism rather than several and are also less costly because they are available in generic formulations.
The campaign aims to address the twin challenge of resisting the use of antibiotics (especially those in Watch and Reserve list) to prevent the development of AMR and to fill vast gaps in access to effective and appropriate antibiotics at many low- and middle-income countries