Atmospheric Stability and Instability
Atmospheric stability and instability refer to the behavior of air in the Earth’s atmosphere, which is influenced by a range of factors, including temperature, pressure, and humidity. Understanding these concepts is critical for predicting changes in weather patterns and developing strategies for mitigating the effects of severe weather events
What is Atmospheric Stability and Instability?
Atmospheric stability and instability refer to the behavior of air in the Earth’s atmosphere. Stable air is characterized by a tendency to resist vertical motion, while unstable air is characterized by a tendency to rise and form clouds and precipitation.
Factors that Influence Atmospheric Stability and Instability
Atmospheric stability and instability are influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Temperature: Warm air is less dense than cold air and tends to rise, while cold air is denser and tends to sink. This creates differences in pressure that can lead to the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- Pressure: High pressure systems are associated with stable atmospheric conditions, while low pressure systems are associated with unstable conditions and the potential for storms and severe weather.
- Humidity: The amount of moisture in the air can affect atmospheric stability and instability, with moist air being more likely to rise and form clouds and precipitation.
- Topography: Mountain ranges and other topographic features can affect atmospheric stability and instability by forcing air to rise or sink and creating areas of high and low pressure.
Understanding Atmospheric Stability and Instability
Atmospheric stability and instability are important concepts in meteorology and climatology, as they are critical for predicting changes in weather patterns and developing strategies for mitigating the effects of severe weather events.
Stable Atmosphere
A stable atmosphere is characterized by a tendency to resist vertical motion. This means that air parcels that are lifted from the surface will tend to return to their original location, rather than continuing to rise and form clouds and precipitation. Stable atmospheric conditions are associated with high pressure systems, which are typically associated with fair weather and clear skies.
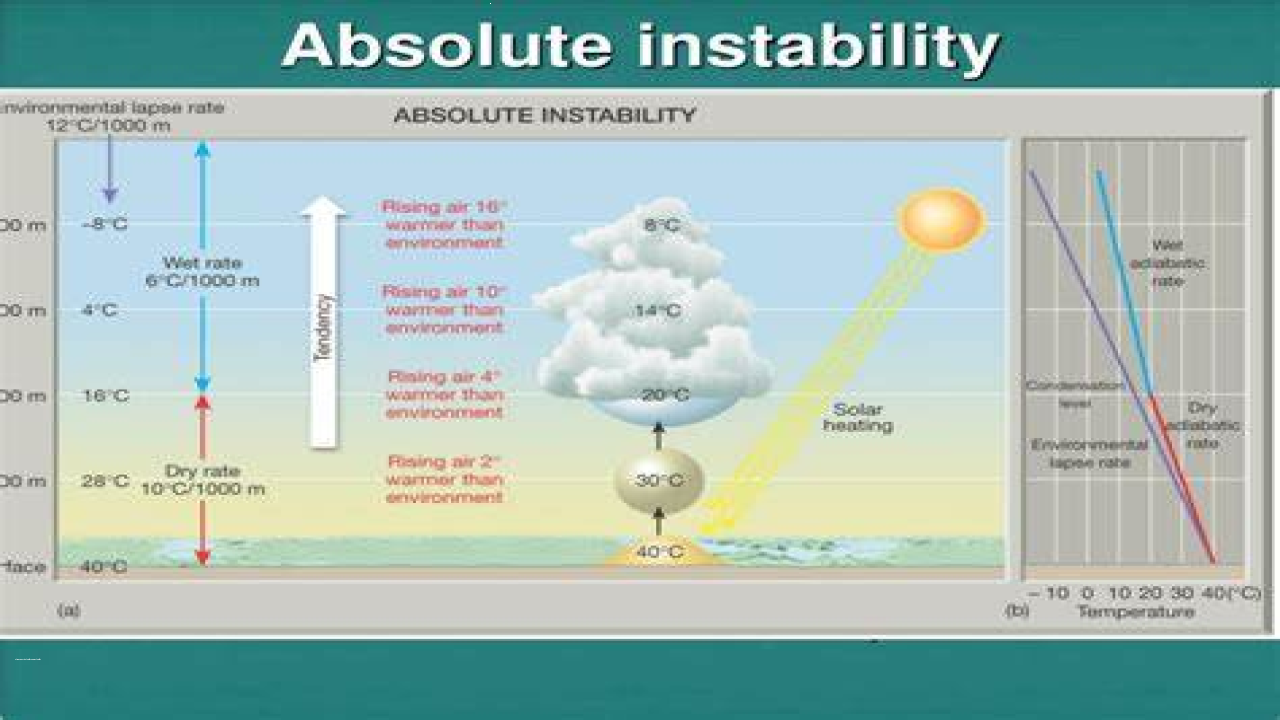
Unstable Atmosphere
An unstable atmosphere is characterized by a tendency to rise and form clouds and precipitation. This means that air parcels that are lifted from the surface will continue to rise, cooling and condensing to form clouds and potentially leading to the formation of thunderstorms or other severe weather events. Unstable atmospheric conditions are associated with low pressure systems, which are typically associated with stormy weather and precipitation.
Conditional Instability
Conditional instability occurs when the atmosphere is initially stable, but becomes unstable under certain conditions. This occurs when a layer of warm, moist air is trapped beneath a layer of cool, dry air, creating a situation where the warm air is less dense and has a tendency to rise. Under certain conditions, such as the introduction of a disturbance or the lifting of the cool air layer, this warm air can rise and form clouds and precipitation.