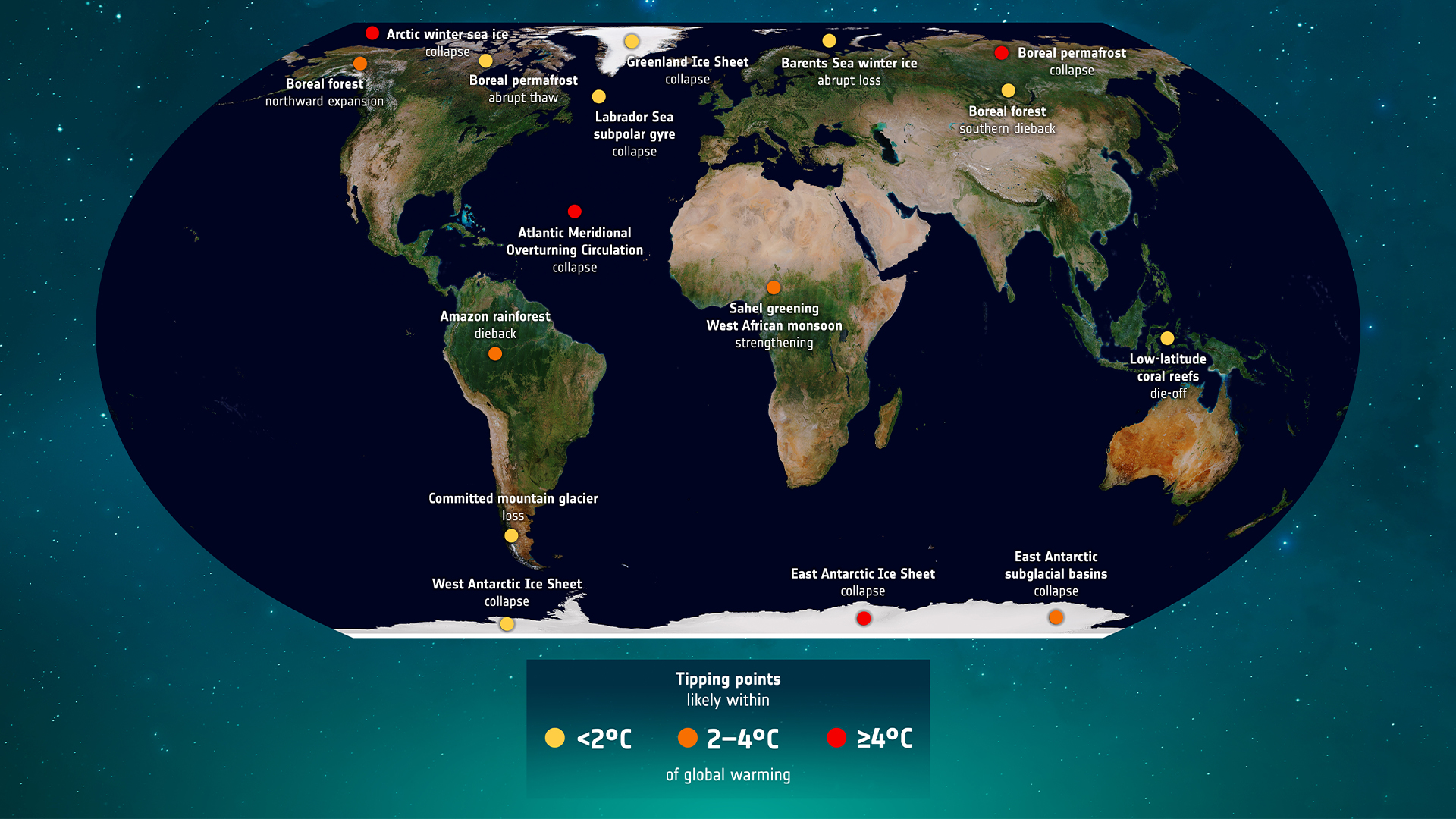
Climate Tipping Points
Recent studies indicate an alarming 62% risk of triggering climate tipping points if current global emission policies persist. These tipping points include phenomena such as the collapse of ice sheets and the death of coral reefs. Researchers from the universities of Exeter and Hamburg conducted a comprehensive analysis of 16 critical areas within the Earth system. Their findings tell the urgency of reducing greenhouse gas emissions to avert irreversible damage to ecosystems and human societies. However, they also highlight that adopting more sustainable practices could reduce this risk to 37%.
About Climate Tipping Points
A climate tipping point refers to a critical threshold where a minor change can lead to and often irreversible impacts on the climate system. Examples include the melting of polar ice caps, the dieback of forests, and the degradation of coral reefs. Once these points are crossed, the resulting changes can cascade through the ecosystem, leading to widespread consequences.
Current Research Findings
The recent study assessed potential tipping points under various emission scenarios – low, medium, and high. The most conservative estimate shows a 62% average risk of triggering these tipping points based on ongoing emissions. Notably, the Amazon rainforest faces a 53% chance of reaching a tipping point, which could have catastrophic effects on biodiversity and climate regulation.
Impact of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. This warming can accelerate the melting of ice sheets and the degradation of ecosystems. The study suggests that if emissions continue unchecked, the consequences will be abrupt and irreversible, posing severe risks to both the environment and humanity.
Potential for Mitigation
The researchers found that with swift action to reduce emissions, the risk of triggering tipping points could be lowered to 37%. This finding presents a glimmer of hope, indicating that proactive measures can still make a difference. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable land management practices are crucial steps in this direction.
Urgency of Global Action
The study emphasises the critical need for immediate global climate action. The risks of crossing tipping points are not distant threats; they are imminent and will be determined in the coming decades. The authors advocate for rapid policy changes and increased efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to safeguard the planet’s future.
Month: Current Affairs - April, 2025
Category: Environment Current Affairs