India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor Developments
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) is gaining momentum with recent initiatives by RITES. This project aims to enhance trade and connectivity between India and the Middle East, and further into Europe. RITES is now focusing on creating a digital interface to facilitate cargo clearance between Indian and Middle Eastern ports. This will mark the first phase of a virtual trade corridor.
Digital Interface Connectivity Project
RITES is developing software for seamless cargo clearances. This initiative includes improving the ease of doing business in cargo export-import procedures. The project will integrate IT systems and logistics support. This digital interface will streamline documentation and clearances across multiple ports.
Interlinking Payment Systems
India and the UAE have signed agreements to interlink their payment platforms. This includes the integration of UPI from India with AANI from the UAE. Such measures will enable smooth cross-border transactions. Additionally, the interlinking of RuPay and JAYWAN debit/credit cards will enhance financial cooperation between the two nations.
What is IMEC?
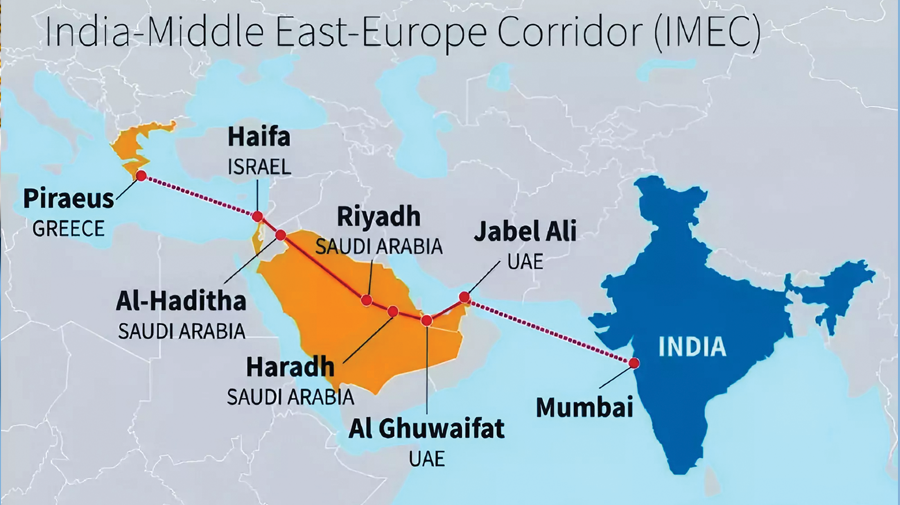
- A new 4,800 km trade and transport corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- It will consist of ship-to-rail networks and road transport routes.
- The corridor was announced in September 2023.
- It is viewed strategically as a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- It will include rail, road, and sea routes across two corridors:
- East Corridor: Links India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Connects the Gulf to Europe.
- Infrastructure includes an electricity cable, hydrogen pipeline, and high-speed data cable.
- India, USA, Saudi Arabia, UAE, European Union, Italy, France, Germany are its signatories.
- RITES has signed an MoU with Abu Dhabi Ports Group and Etihad Rail to explore rail connectivity.
Key Ports Connected
- India: Mundra, Kandla (Gujarat), JNPT (Navi Mumbai).
- Middle East: UAE (Fujairah, Jebel Ali, Abu Dhabi), Saudi Arabia (Dammam, Ras Al Khair).
- Israel: Haifa port (connected via Saudi Arabia and Jordan).
- Europe: Greece (Piraeus), Italy (Messina), France (Marseille).
Objectives of IMEC
- Create a fast and efficient transport network between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Reduce costs, improve trade efficiency, and cut Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions.
- Strengthen economic ties and generate employment opportunities.
Geopolitical & Economic Implications of IMEC
Geopolitical Impact
- Counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): IMEC provides an alternative trade route, reducing reliance on China’s infrastructure projects.
- Stronger International Ties: Strengthens connections between Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. Reinforces the US’s presence in the region.
- Bypassing Pakistan: Helps India avoid Pakistan’s blockade on direct land connectivity to the West.
- Deeper Ties with the Arabian Peninsula: Strengthens India’s political and economic relationships with Gulf nations.
- Promoting Peace and Stability: Improved regional connectivity may help reduce tensions in the Middle East.
- Potential Expansion to Africa: Aligns with the US and EU’s plans to develop a Trans-African corridor, allowing India to play a bigger role in Africa’s infrastructure growth.
Economic Impact
- Boosts Trade & Reduces Transit Time: IMEC shortens India-Europe trade routes by 40% compared to the Suez Canal.
- Encourages Industrial Growth: Companies can easily transport goods, boosting industrial activity.
- Creates Jobs: Expands employment in infrastructure, trade, and logistics.
- Strengthens Energy Security: Ensures stable access to energy resources from the Middle East.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs): IMEC can help develop industrial hubs along its route, attracting foreign investment.
Challenges Facing IMEC
- Logistics & Connectivity Issues: Coordinating rail, road, and sea transport across multiple countries is complex.
- Missing Rail Links: Many rail connections, especially in the Middle East, are incomplete.
- Coordination Among Countries: Managing different legal systems, policies, and interests is challenging.
- Competition from Existing Routes: The Suez Canal may resist IMEC as it threatens its trade dominance.
- High Costs: Developing IMEC could cost $3 billion to $8 billion, requiring massive funding.
Infrastructure Development
RITES is identifying infrastructure gaps to connect West Coast ports to the Dedicated Freight Corridor. This includes the upcoming Vadhavan Port. The goal is to enhance logistics and supply chain efficiency.
Overseas Expansion and Export Growth
RITES is exploring project consultancy opportunities in the Middle East. The company is also focusing on rolling stock exports to Latin America and Bangladesh. RITES is aggressively bidding for export projects without relying on Line of Credit options.
Month: Current Affairs - January, 2025
Category: Economy & Banking Current Affairs