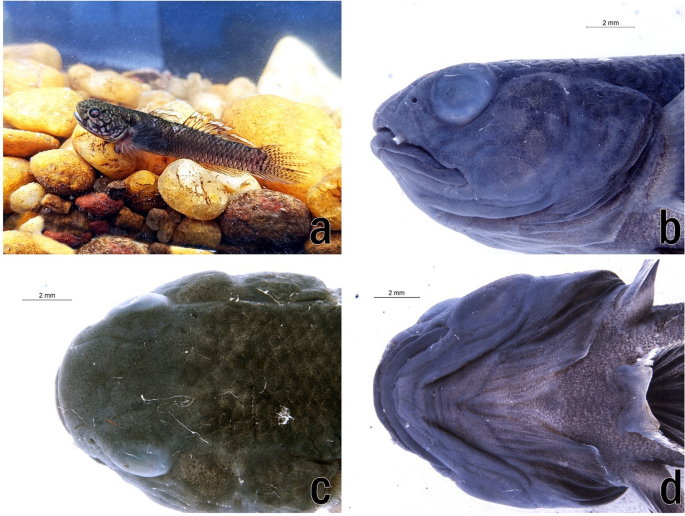
Goby Fish Discovery in Andhra
Recently, researchers from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) made a notable discovery at the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh. They identified two previously unrecorded species of goby fish, Hemigobius hoevenii and Mugilogobius tigrinus. This finding marks the first time M. tigrinus has been documented along India’s eastern coastline, denoting the importance of mangrove ecosystems.
Significance of Goby Fish
- Goby fish are vital to estuarine ecosystems.
- They serve as indicators of environmental health and occupy various levels in the food chain, contributing to ecological balance.
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary
- Coringa is the third largest mangrove forest in India, located near Kakinada.
- It features 24 species of mangrove trees and over 120 bird species, including critically endangered vultures.
Research Findings
The ZSI researchers found that 95 out of 135 goby species recorded in India inhabit mangroves. The sanctuary is home to 53 of these species, indicating rich biodiversity.
Mangrove Ecosystems
Mangroves are coastal trees that thrive in intertidal zones. Their complex root systems protect shorelines from erosion and provide habitats for various marine life.
Challenges to Biodiversity
Access issues and pollution near estuaries hinder research on goby fish. Waste disposal impacts species diversity, threatening ecological stability in these habitats.
Future Research Directions
The discovery encourages further exploration of mangrove ecosystems in India. Other mangrove areas, like the Sundarbans and Andaman Islands, require more research to uncover hidden biodiversity.
Global Context
Globally, there are 5,561 known goby species. India’s goby diversity is relatively low, with ongoing research needed to understand the full extent of species in its mangrove forests.
Month: Current Affairs - January, 2025
Category: Environment Current Affairs