The Homo Juluensis Discovery: A New Chapter
Recent research has revealed a long-lost human species named Homo juluensis, which could reshape our understanding of human evolution. Scientists previously viewed evolution as a linear process and new findings suggest a more complex evolutionary tree.
Background on Homo Juluensis
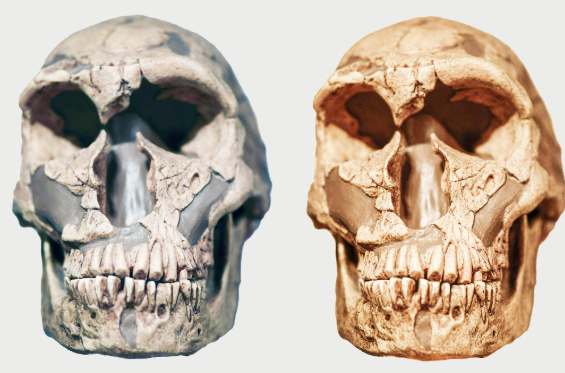
Homo juluensis existed around 300,000 years ago and they lived in eastern Asia and thrived in small groups. This species vanished approximately 50,000 years ago. Their large skulls earned them the nickname “big-head people.”
Coexisting Human Species
Four distinct human species coexisted in eastern Asia. These included Homo floresiensis, Homo luzonensis, Homo longi, and Homo juluensis. Homo floresiensis and Homo luzonensis were small and compact. In contrast, Homo longi and Homo juluensis had larger skulls.
The research indicates these species interacted with one another. They likely mixed and exchanged traits over time. This challenges the notion of isolated human evolution.
Implications for Human Evolution Studies
The findings help clarify the diversity of ancient humans in Asia. They offer a new framework for studying Asian hominin fossils. Christopher Bae emphasised the importance of this discovery. He noted that Asia has been less studied than Europe and Africa.
Limitations of the Research
Despite the breakthrough, many fossils remain incomplete. Researchers still seek to understand genetic links among these species. This discovery is step but needs further evidence.
Further investigation is necessary to validate these findings. More fossil discoveries could provide additional insights. About Homo juluensis may lead to a deeper comprehension of human evolution.
GKToday Facts for Exams:
- Homo juluensis This long-lost species existed around 300,000 years ago. Known as the “big-head people,” they thrived in small groups across eastern Asia before disappearing 50,000 years ago.
- Homo floresiensis Often called “hobbits,” Homo floresiensis were a distinct human species. They were notably small and compact, coexisting with other human species in eastern Asia during the same period.
- Paleoanthropologists Paleoanthropologists study ancient human species and their evolution. Researchers like Christopher Bae and Xiujie are reshaping our understanding of human evolution through fossil discoveries in eastern Asia.
- Quaternary Era The Quaternary era began around 2.58 million years ago. It is characterised by climate changes and the evolution of many modern species, including various human ancestors.
Month: Current Affairs - December, 2024
Category: Science & Technology Current Affairs