What is ecDNA?
Extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) has gained attention in cancer research. Recent studies have found it in many types of tumours, showing its key role in cancer biology.
Discovery and Importance
ecDNA was discovered 50 years ago as a small genetic fragment in cancer cells. Initially, it was thought to appear in only 1.4% of tumours. Advanced research now indicates ecDNA is found in up to 90% of certain brain tumours. This marks its essential role in cancer progression.
Formation of ecDNA
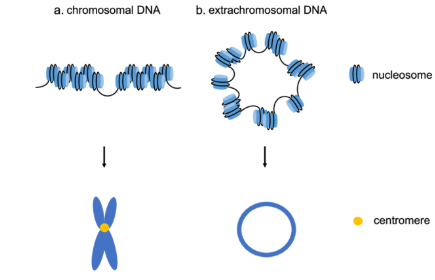
In normal cells, DNA is organised within 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus. Damage from smoking or environmental factors can cause DNA to break. This broken DNA may form a circular structure, leading to ecDNA. Unlike chromosomal DNA, ecDNA can move freely and cluster with other ecDNA.
The mobility of ecDNA enhances the expression of oncogenes. This contributes to faster tumour growth. It also aids in developing resistance to treatments like chemotherapy. A study found ecDNA in 17% of tumour samples from nearly 15,000 cancer patients.
Inheritance and Survival Advantage
ecDNA violates Mendel’s third law of inheritance. It is inherited in clusters during cell division. This gives cancer cells an advantage by preserving beneficial genetic combinations that promote growth.
Therapeutic Potential
Despite its risks, ecDNA presents a potential weakness in cancer cells. Its structure increases gene activity, stressing the cell’s DNA repair system. Blocking the CHK1 protein can selectively kill cancer cells with ecDNA. Boundless Bio is developing treatments targeting ecDNA-driven cancers like glioblastoma, ovarian, and lung cancers.
These findings may lead to new therapies targeting ecDNA. About its role could improve treatment outcomes for various cancers. Research continues to explore effective strategies against ecDNA-related challenges.
Important Facts for Exams:
- ecDNA: Extrachromosomal DNA is a small, circular genetic fragment found in cancer cells. It enhances oncogene expression, contributing to tumour growth and resistance against chemotherapy treatments.
- CHK1: CHK1 is a DNA repair protein that, when blocked, selectively kills cancer cells with ecDNA. This mechanism shows potential for developing targeted cancer therapies.
- Boundless Bio: Boundless Bio is a biotechnology company focused on targeting ecDNA-driven cancers. Their research aims to develop novel treatments for glioblastoma, ovarian, and lung cancers.
- Mendel’s third law: Mendel’s third law states that genes are inherited independently. However, ecDNA violates this law by clustering during cell division, giving cancer cells a survival advantage.
Month: Current Affairs - December, 2024
Category: Science & Technology Current Affairs