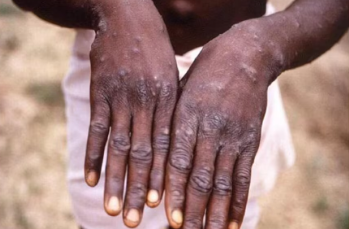
Mpox Virus – Recent Developments and Concerns
The mpox virus, previously known as monkeypox, has remained an important public health concern since the eradication of smallpox in 1980. In 2022 and again in 2023, the World Health Organisation (WHO) declared mpox a public health emergency. This marks the ongoing threat posed by this virus, especially in West and Central Africa.
About Mpox Clades
Mpox consists of two main clades – I and II. Clade I is known for causing severe disease in animal models, while Clade II has been responsible for recent outbreaks. Each clade is further divided into subclades – Ia, Ib, IIa, and IIb. Clade IIb was the primary cause of the 2022 outbreak, still active in parts of Africa. Clade Ib emerged in late 2023 as an important concern in Central Africa.
Human-to-Human Transmission
Historically, clade Ia caused sporadic infections primarily from animals to humans. Recent studies, however, indicate a shift. Evidence shows that clade Ia viruses are now capable of human-to-human transmission. This change raises alarms regarding the virus’s evolution and potential spread.
Virus Mutations and Evolution
Viruses evolve through mutations during replication. The polymerase enzyme copies the viral genetic material but can introduce errors. These mutations can impact the virus’s behaviour, with varying rates across different types. Poxviruses, including mpox, have a lower mutation rate due to their proofreading mechanisms.
Role of APOBEC Proteins
APOBEC proteins can introduce additional mutations in viral DNA during replication. These changes can potentially hinder the virus’s ability to replicate. Recent research suggests that APOBEC activity has increased the mutation rate of circulating mpox strains. This indicates that the virus has adapted to human hosts.
Implications for Vaccination Strategies
The emergence of human-to-human transmission in clade Ia is concerning but may not alter current vaccination strategies. However, different mpox clades respond variably to antiviral treatments. This variability complicates public health responses and necessitates ongoing surveillance and research.
Current Vaccination Efforts
In response to the outbreaks, affected African nations have begun targeted vaccination campaigns. However, limited vaccine supplies have forced prioritisation among countries. The effectiveness of these campaigns is critical in controlling the spread of mpox.
Future Research Directions
Ongoing research is essential to understand the dynamics of mpox transmission and mutation. Studies should focus on the implications of clade Ia’s human-to-human transmission. About the virus’s evolution will aid in developing effective treatments and vaccines.
The situation surrounding mpox remains fluid. Continuous monitoring and adaptive strategies will be crucial in combating this evolving public health threat.
Important Facts for Exams:
- APOBEC: APOBEC stands for apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like. It introduces mutations in viral DNA helping to combat viral replication and evolution.
- Clade IIb: Clade IIb of the mpox virus was responsible for the 2022 outbreak. It continues to circulate in certain parts of Africa raising concerns about public health.
- Virologica: Virologica is an online scientists’ discussion forum. It serves as a platform for researchers to share preprint papers and findings on virology and related topics.
- Clade Ia: Clade Ia is the oldest variant of the mpox virus. It has caused sporadic infections in humans since 1970 primarily through animal-to-human transmission.
Month: Current Affairs - November, 2024
Category: Science & Technology Current Affairs