What is Legionnaires’ Disease?
A rising outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease in Victoria, Australia has caused concern among health officials. The number of confirmed cases has increased from 22 to 33, with an additional 10 cases suspected. Chief Health Officer Clare Looker has noted a troubling rise in cases, mostly in the northern and western suburbs of Melbourne.
Understanding Legionnaires’ Disease
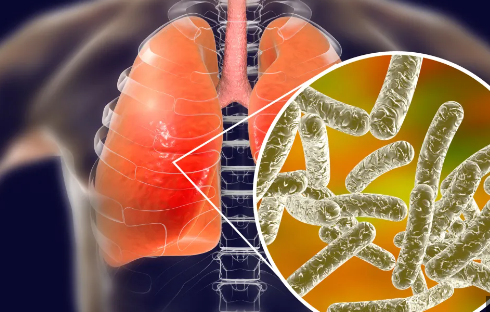
Legionnaires’ disease is a serious type of pneumonia caused by the Legionella bacteria. It usually happens when people breathe in water droplets contaminated with these bacteria. This contamination often comes from sources like air-conditioning systems, spas, and misting devices.
Transmission Information
The disease is not spread from person to person. Instead, people get infected through environmental sources, particularly from aerosols created by cooling towers or similar equipment.
Current Health Advisory
Authorities are advising people in metropolitan Melbourne to watch for symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, headaches, and muscle aches. If someone has these symptoms, they should seek medical help as soon as possible. People over 40 years old, especially those with existing health conditions or weakened immune systems, are at the highest risk. Dr. Looker stressed the importance of monitoring the health of these vulnerable groups. Investigators are trying to find the source of the outbreak. They suspect that a cooling tower might be involved but are also considering other possibilities. Efforts to trace contacts and identify the source are ongoing.
About Legionnaires’ disease
- Cause and Discovery: Legionnaires’ disease is caused by Legionella bacteria and was first identified after an outbreak at a 1976 American Legion convention.
- Symptoms and Sources: It mainly affects the lungs, causing pneumonia-like symptoms, and the bacteria grow in warm water sources like hot tubs and cooling towers.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Symptoms show up 2 to 10 days after exposure and include cough, fever, and muscle aches. It’s diagnosed with urine tests or lung imaging and treated with antibiotics, but it can be deadly for vulnerable people.
Month: Current Affairs - August, 2024
Category: International / World Current Affairs