Applied Climatology and Urban Climate
Applied climatology is the study of how climate information can be used to inform decision-making in a range of fields, including agriculture, water management, and urban planning. Urban climate, on the other hand, focuses on the specific climate conditions found in urban environments and the impacts of human activity on those conditions.
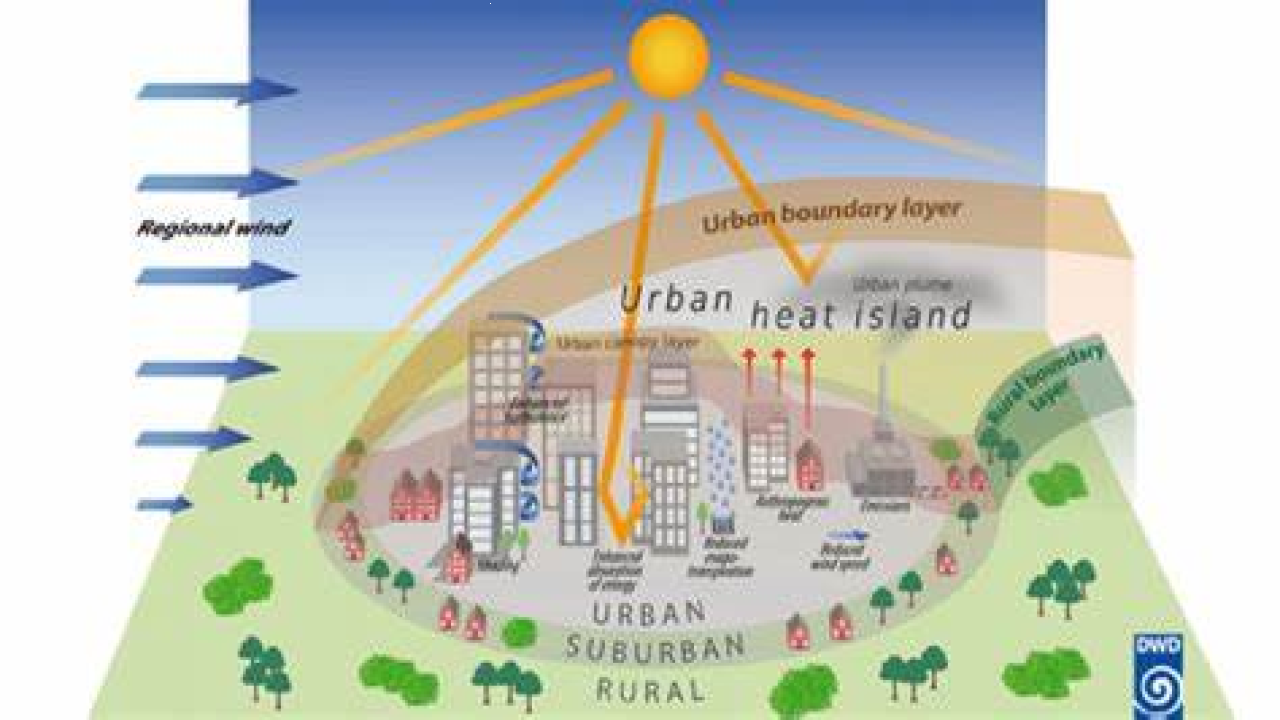
The Urban Heat Island Effect
One of the most significant impacts of human activity on urban climate is the urban heat island effect. This occurs when urban areas are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas, due to factors such as the presence of buildings and pavement, reduced vegetation cover, and increased human activity.
The urban heat island effect can have significant impacts on human health and well-being, with increased risk of heat-related illnesses and mortality. It can also lead to increased energy consumption for cooling, as well as impacts on infrastructure and transportation systems.
Urban Planning and Design
Urban planning and design can play an important role in addressing the impacts of the urban heat island effect and promoting sustainable urban environments. Strategies such as increasing vegetation cover, promoting green roofs and walls, and improving building design and orientation can help to reduce urban temperatures and improve air quality.
Urban planning and design can also be informed by climate information, such as temperature and precipitation patterns, to help identify areas at risk of flooding, extreme heat, and other climate-related impacts.
Climate and Water Management
Applied climatology is also essential for managing water resources in urban environments. Climate information can be used to inform decisions around water supply and demand, as well as flood and drought risk management.
In addition, urban environments can have significant impacts on local hydrological cycles, with increased impervious surfaces leading to increased runoff and reduced infiltration. Sustainable water management strategies, such as green infrastructure and water recycling, can help to mitigate these impacts and promote more resilient urban water systems.
Climate and Energy Management
Climate information can also be used to inform energy management strategies in urban environments. This includes strategies such as reducing energy demand through energy efficiency measures and promoting renewable energy technologies, as well as improving energy system resilience in the face of climate-related risks.
Urban environments can also have significant impacts on local and regional air quality, with increased levels of air pollution leading to negative impacts on human health and well-being. Strategies such as promoting low-emission transportation options and reducing energy consumption can help to improve air quality and promote more sustainable urban environments.