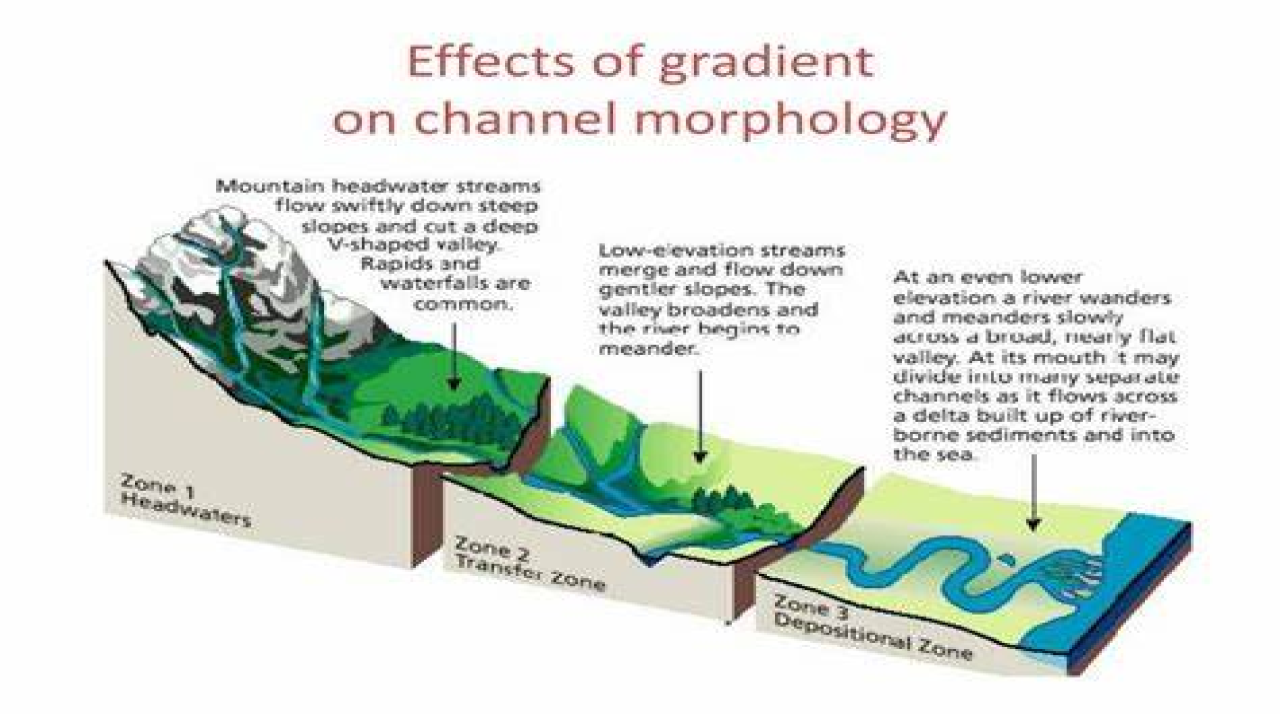
Channel morphology
Channel morphology refers to the physical characteristics of river channels, including their shape, size, and behavior. The study of channel morphology is important for understanding how rivers function and how they are impacted by natural and human-induced changes. In this article, we will explore channel morphology in more detail, including its importance, the factors that influence it, and the methods used to study it.
Importance of Channel Morphology
Channel morphology is important because it influences the behavior of rivers and the ecosystems that they support. The shape and size of river channels determine the speed and direction of water flow, the types of habitats that are present, and the types of sediment that are transported downstream. Changes in channel morphology can have significant impacts on river ecosystems, including changes in the types of plant and animal species that are present and changes in the quality and quantity of water that is available.
Factors that Influence Channel Morphology
Several factors influence channel morphology, including the type of bedrock, the climate, the amount and type of sediment that is present, and human activities such as channelization and dam construction.
- Bedrock Type: The type of bedrock that is present in a river channel can have a significant impact on channel morphology. For example, soft sedimentary rocks are more easily eroded than hard igneous or metamorphic rocks, which can lead to wider and shallower channels.
- Climate: The climate of a region can influence the shape and behavior of river channels. For example, areas with high rainfall tend to have more erosive rivers with deeper channels, while areas with lower rainfall tend to have less erosive rivers with shallower channels.
- Sediment: The amount and type of sediment that is present in a river channel can also influence channel morphology. For example, rivers that transport large amounts of coarse sediment tend to have steeper channels and faster water flow, while rivers that transport finer sediment tend to have gentler channels and slower water flow.
- Human Activities: Human activities such as channelization and dam construction can also impact channel morphology. Channelization involves altering the shape and size of river channels to control water flow and reduce flooding. This can lead to changes in the types of habitats that are present and the types of sediment that are transported downstream. Dam construction can also impact channel morphology by altering the amount and timing of water flow, which can lead to changes in sediment transport and erosion rates.
Methods Used to Study Channel Morphology
Several methods are used to study channel morphology, including field surveys, remote sensing, and numerical modeling.
- Field Surveys: Field surveys involve collecting data on the shape and size of river channels using methods such as cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal profiles, and sediment sampling. This data can be used to calculate parameters such as channel width, depth, slope, and sediment transport rates.
- Remote Sensing: Remote sensing involves using satellite or aerial imagery to gather information on channel morphology. This can be done using methods such as LiDAR, which uses lasers to measure the elevation of the land surface, and photogrammetry, which uses photographs to create three-dimensional models of the landscape.
- Numerical Modeling: Numerical modeling involves using computer simulations to predict the behavior of river channels under different conditions. This can be done using methods such as hydraulic models, which simulate water flow, and sediment transport models, which simulate the movement of sediment.