What is a ‘Sponge city’ in Water Management?
Chennai is all set to adopt innovative water management strategies and transform into a sponge city to curb the urban flooding.
Key Points
- Sponge city concept seeks to make urban areas more permeable, have more open spaces to store rainwater as well to allow it to percolate to aquifers.
- Water Resources Department in Chennai is looking over possibility of digging recharge shafts in smaller water bodies across the city.
- These recharge shafts can be dug up to a depth of 80-90 feet. It will help replenish water table.
- As per plan, smaller water bodies & temple tanks could be used as structures for storing surplus water during intense rain. Water can be treated, drawn, and supplied to the city as per need.
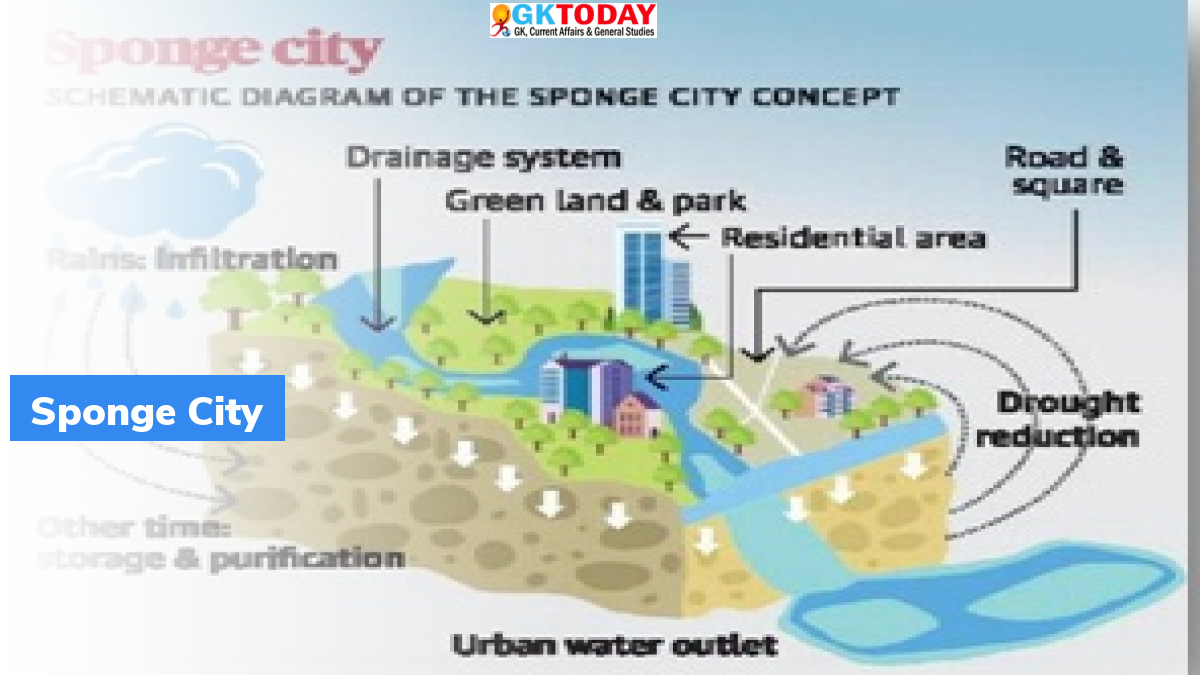
What is a sponge city?
Sponge city is a new urban construction model for flood management, and to strengthen ecological infrastructure & drainage systems. This concept was proposed by Chinese researchers in 2000. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and State Council accepted this concept as “urbanism policy” in 2014. This system helps in alleviating urban flooding, urban heat island effect and water resources shortage. It also improves the ecological environment and biodiversity by absorbing & capturing rain water and using it to reduce floods. Sponge city policies are nature-based solutions, which use natural landscapes for catching, storing and cleaning water. This concept was inspired by ancient wisdom of adaptation to climate challenges, specifically in monsoon world.
Sponge Cities Mission – In India
The main idea of the sponge city is to make cities more permeable in order to hold and use water which falls upon it. These can all be delivered effectively by an urban mission along the lines of National Heritage City Development & Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY), Atal Mission for Rejuvenation & Urban Transformation (AMRUT), and Smart Cities Mission.
What is the need of Sponge Cities Mission in India?
In India, there is a need of Sponge cities because,
- Urban flooding has become recurring phenomenon in Indian metros.
- India’s Land policy has not been effective in managing or controlling the recurrence of major floods in urban areas.
- Urban cities lack proper drainage network.
- Concrete structures in urban cities are causing water wastage.
Month: Current Affairs - December, 2021